
(iii) All aliphatic amines are more basic than ammonia. (ii) Because of the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of - N ˙ H ˙ 2 group, amines behave as Lewis bases.

Additionally, your unknown compound may or may not contain. contain an amide group a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group where the -OH. The results showed that two main factors, the orientation of the amide functional group and the part of the amide frame exposed to the aromatic zone of the asphaltene, had an important effect on. It is the isomer of the related cyanide (-CN). (i) The order of boiling points of isomeric amines is primary > secondary > tertiary. one major functional group (alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, amide, amine, carboxylic acid, or ester). functional group: an atom, or group of atoms (with specific connectivity). An isocyanide (also called isonitrile or carbylamine) is an organic compound with the functional group -NC. Physical and chemical properties of amines: (organic chemistry) Any organic compound containing an amine functional group. (vii) Hoffmann bromamide degradation reactionģ. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amine. (vi) Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of primary amines. R - N + H 3 X - + NaOH → R - NH 2 + H 2 O + N + a X.
In simple amides, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to the nitrogen (-CONH2) while in more complex amides, the nitrogen is bonded to one or two aliphatic or aromatic groups (-CONR). Also, hydrogen bonding affects their spectra. They are unusual in that they contain nitrogen and a carbonyl group, giving a number of useful group wavenumbers.
#Amide functional group free#
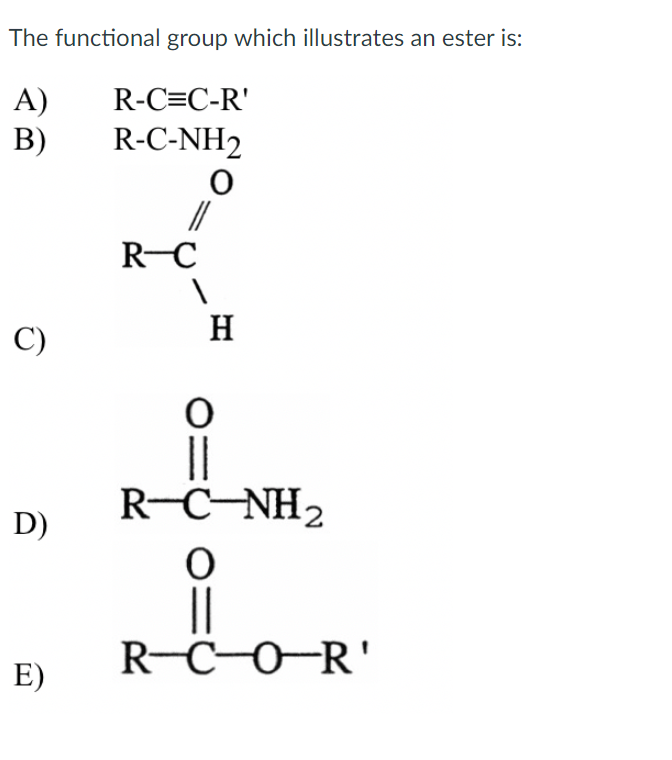
(iii) The free amine can be obtained from the ammonium salt by treatment with a strong base. The amide bond is characterized by its thermodynamic stability and kinetic tolerance toward hydrolytic cleavage, which arises from conjugation via the planar O. An amide functional group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen. Amides are an important functional group, because they are found extensively in polymers and proteins. Amines can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, obtained by replacement of one, two or all the three hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
